Introduction to Web3
Web3 is the next iteration of the internet, built on blockchain technology and communally controlled by its users. It aims to decentralize power, giving users control over their data and online identities. To understand Web3, it’s helpful to look at its predecessors: Web1 and Web2.

The Evolution from Web1 to Web3
Web1: This was the initial phase of the internet, characterized by static pages that users could only read. It was the era of the read-only web, with minimal interactivity and content primarily provided by organizations and companies.
Web2: The early 2000s saw the advent of Web2, or the read/write web. This era was marked by user-generated content and social media platforms like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. Web2 allowed users to interact, share, and create content but centralized control remained with tech giants.
The Goals and Vision of Web3
Web3 aims to address the shortcomings of Web2, such as privacy concerns, data ownership, and centralized control. The core goals of Web3 include:
- Decentralization: Distributing control across a network rather than centralizing it in a few entities.
- Data Ownership: Allowing users to own and control their personal data.
- Enhanced Security and Privacy: Using blockchain technology to secure data and transactions.
- Censorship Resistance: Preventing centralized entities from controlling or censoring content.
How Web3 Works: An Example
Imagine a social media platform built on Web3 principles. Instead of a central server owned by a company like Facebook, the platform is hosted on a decentralized network. Each user has an encrypted wallet that stores their data and identity. Users can post content, interact, and transact without intermediaries. The content is stored immutably on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and preventing unauthorized modifications.
Advantages of Web3
- User Empowerment: Users have control over their data and digital identities.
- Transparency: Blockchain technology ensures all transactions and changes are publicly verifiable.
- Enhanced Security: Decentralized networks are less vulnerable to hacks and breaches compared to centralized servers.
- Censorship Resistance: No single entity can control or censor content on a decentralized network.
Supporting Technologies of Web3
Web3 is supported by several cutting-edge technologies, including:
- Blockchain: The foundational technology that provides decentralization and security.
- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code.
- Decentralized Ledger Technology (DLT): A system for recording transactions that is maintained across several nodes.
- Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI): Enhancing user interactions and automating processes.
- Big Data and Natural Language Processing (NLP): Allowing applications to process and understand large amounts of data in a human-like manner.
Web3 vs. Web2: Key Differences
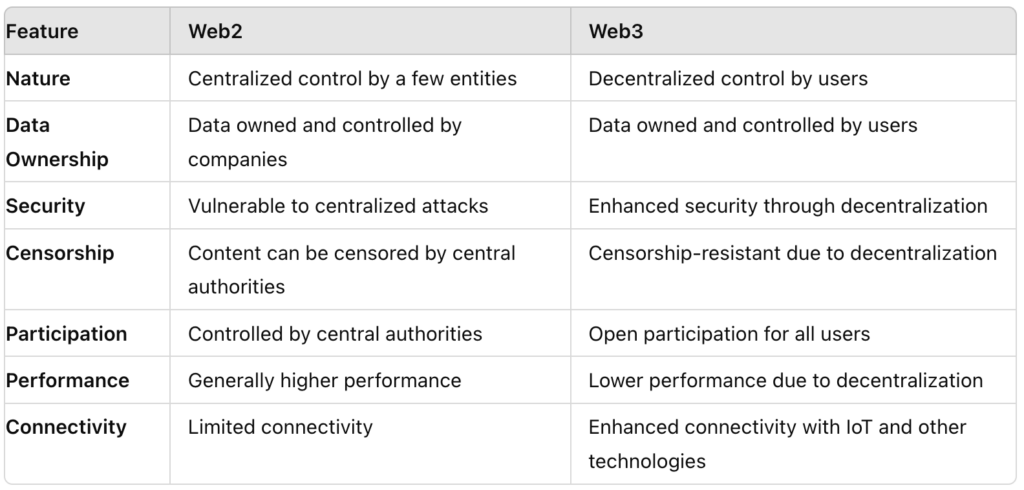
Conclusion
Web3 represents a transformative shift in how we interact with the internet, emphasizing decentralization, user control, and enhanced security. By addressing the limitations of Web2, Web3 aims to create a more open, transparent, and user-centric Internet. As these technologies continue to develop, they hold the potential to redefine our digital experiences and empower users like never before.
Leave a Reply